Test Corrections

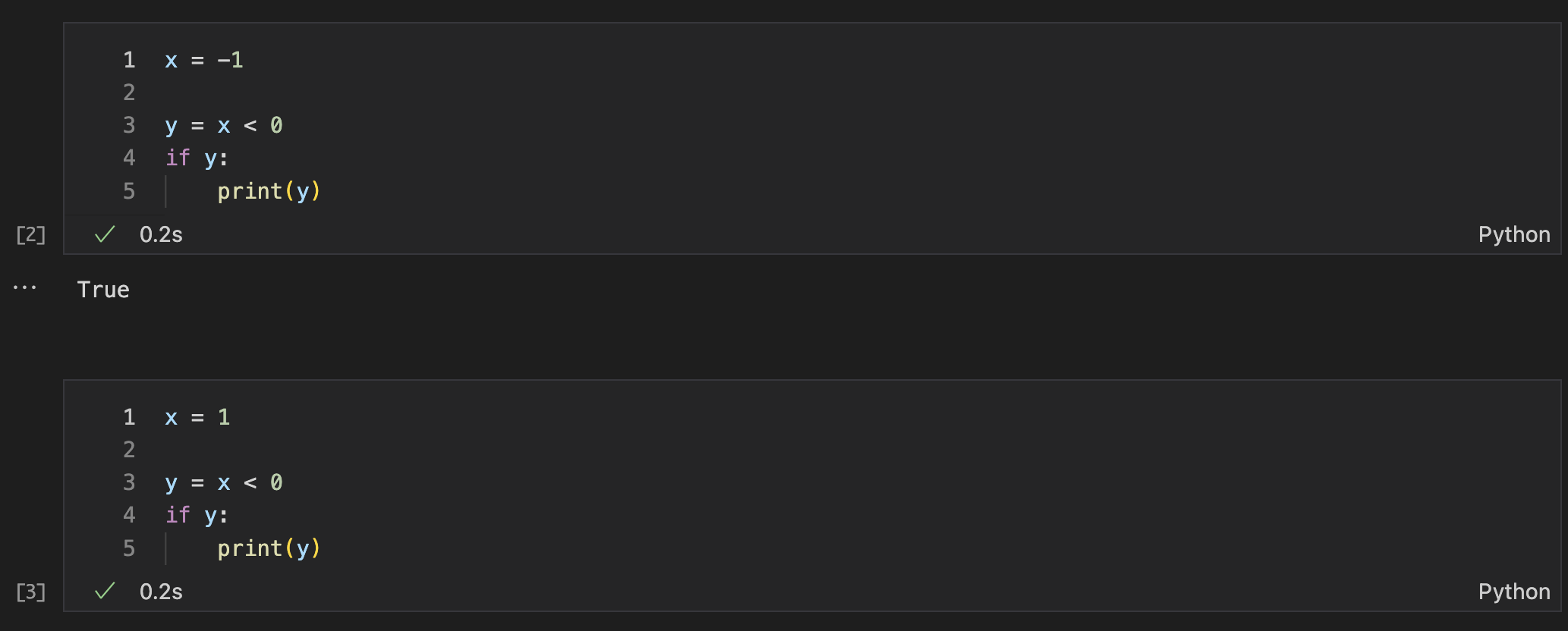
Using Jupyter Notebook, I was able to visualize the code better with an actual output. I thought that having y = False would print “False” but if the if-statement was false, the statement would not print anything.
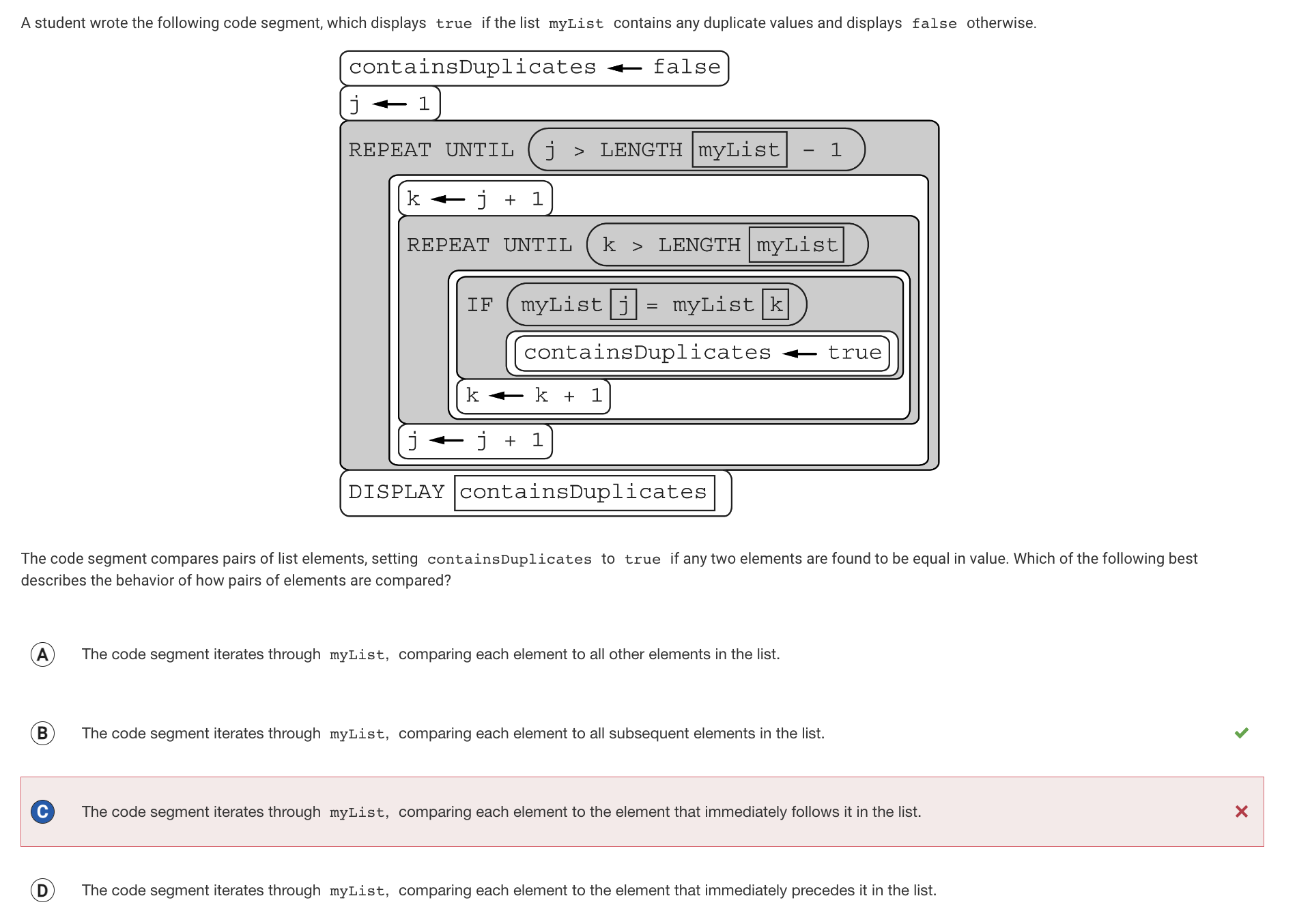
The code first obtains the first index of the list using the variable j. Then it gets another variable k in order to index the other numbers in the rest of the list. The index of the list include len(myList) - 1. The second while loop repeats while changing k and comparing it to the myList(j). The while loop goes on until all the values in the list are looped through.
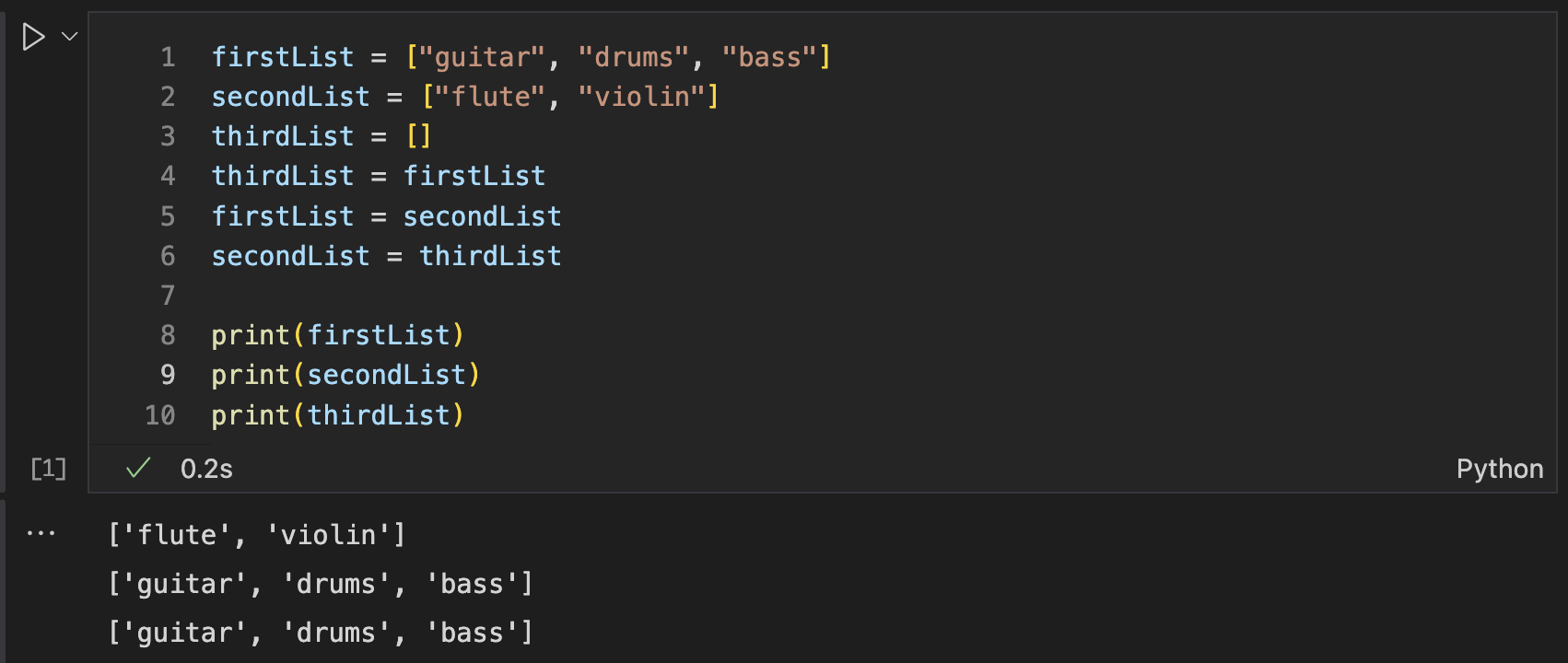
Again, I used Jupyter Notebook to visualize the code. I did not realize that the thirdList had been set to firstList. Then, because secondList was set in thirdList, the secondList = firstList.
Topics to work on:
The Internet
packet: a small amount of data sent over a network; each packet includes the source and destination information
computer system: a group of computing devices and programs working together for a joint purpose
computer network: a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending or receiving data
packet switching: the message (file) is broken up into packets and sent in any order and are reassembled by the recipient’s device
routing: process of finding a path from sender to receiver
path: a sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sender and ends at the receiver
bandwidth: max amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time on a computer network
OSI (Open Systems Interconnect): lays to go through to communicate
TCP (Transmission Control Protcol): establishes a common standard for how to send messages between devices on the internet
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF): manages the development of standards + technical discussions concerning the internet in an open and collaborative process
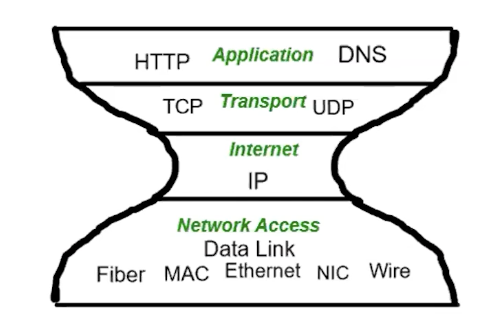
Network Access: hardware related, most common is ethernet
Internet: packets of data + metadata are being transmitted w/ info used for routing information
- internet designed to be scalable- able to change in size and scale to meet demands
- Local Area Network (LAN)- physical connections
- Autonomous Systems (AS)- large intranets linked together under control and policies of major organizations
- the internet- autonomous systems linked together
Transport layer: communicate with hardware and software on the rest of the internet
- FCP (error check + recovery, slower) and UDP (error check, then discard)
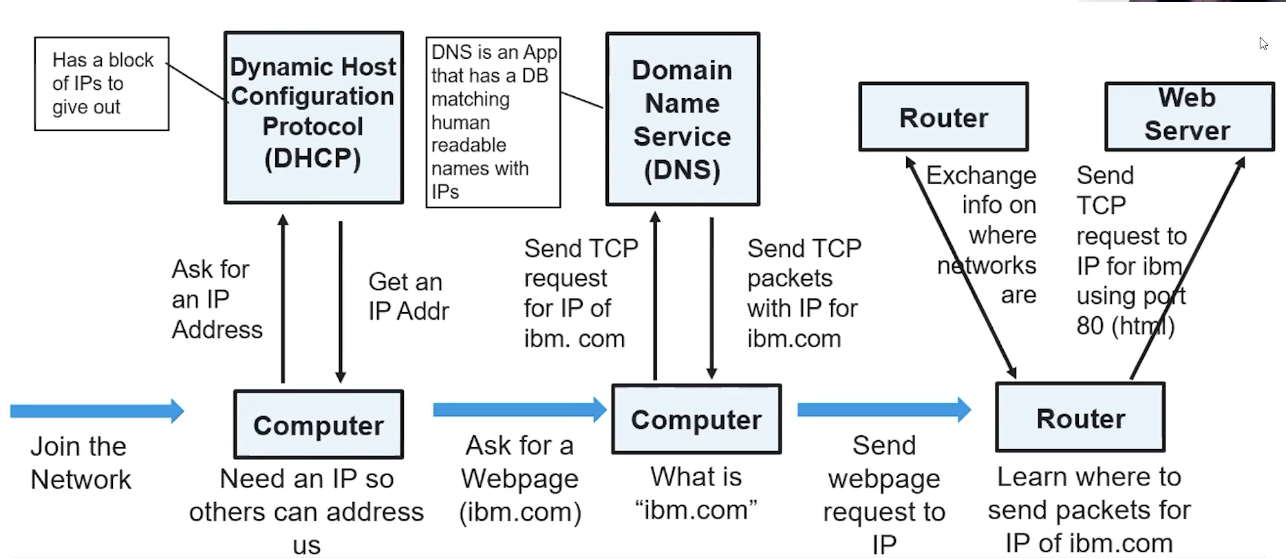
Application: giving a domain name
- DNS
- https is http w/ security
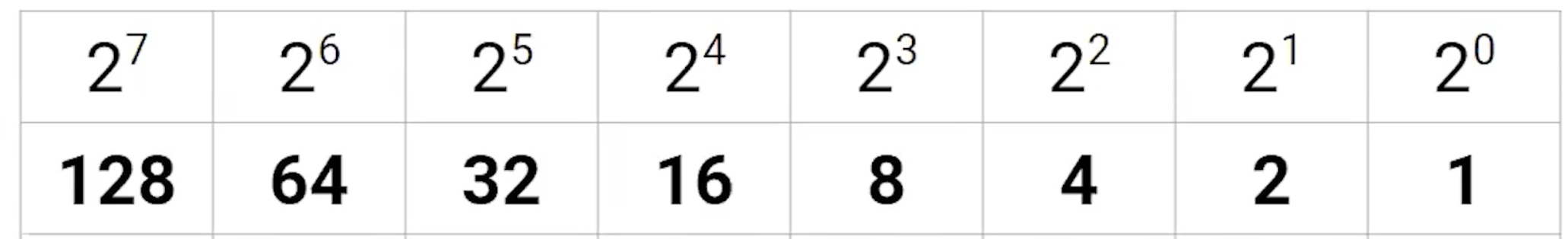
Binary Numbers