| Word |
Definition |
| Variables |
abstraction inside a program that holds a value, where each variable has associated data storage that represents a single value at a time |
| Data Types |
Integral, Floating Point, Character, Character String, and composite types |
| Lists |
a sequence of finite strings that surrounded by square brackets and separated by commas, ex. foods = ["pizza", "watermelon", "sushi", "fried chicken"] |
| Dictionaries |
an abstract data type that defines an unordered collection of data as a set of key-value pairs, ex. capital_city = {"Nepal": "Kathmandu", "Italy": "Rome", "England": "London"} |
| Algorithms |
the algorithm describes the instructions to complete a task, which done by the graphic with a list of instructions to do |
| Sequence |
order of how to do something |
| Selection |
Code that will execute depending on the algorithm condition returning true or false |
| Iteration |
a repeating portion of an algorithm until a given condition is met

|
| Expressions |
syntactic entity in a programming language that may be evaluated to determine its value
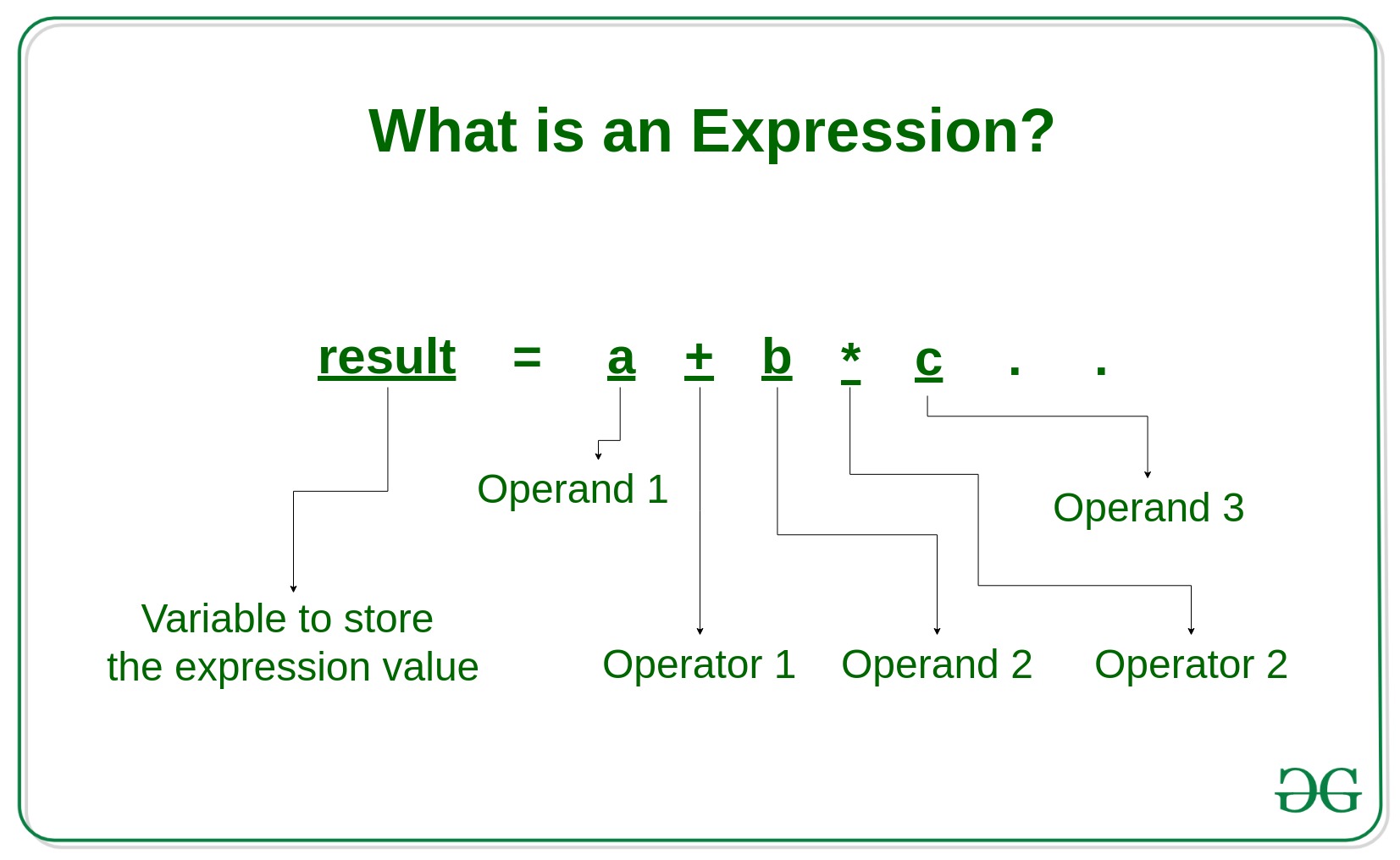
|
| Comparison Operators |
compare numbers or strings and perform evaluations

|
| Truth Tables |

|
| Characters |
a display unit of information equivalent to one alphabetic letter or symbol |
| Strings |
any series of characters that are interpreted literally by a script, ex. "hello world" |
| Length |
Gets length of string or list with len() function |
| Concatenation |
joining two strings together |
| Traversing Strings |
process one character at a time |
| If, Elif, Else conditionals |
Code that is initiated if a statement is true
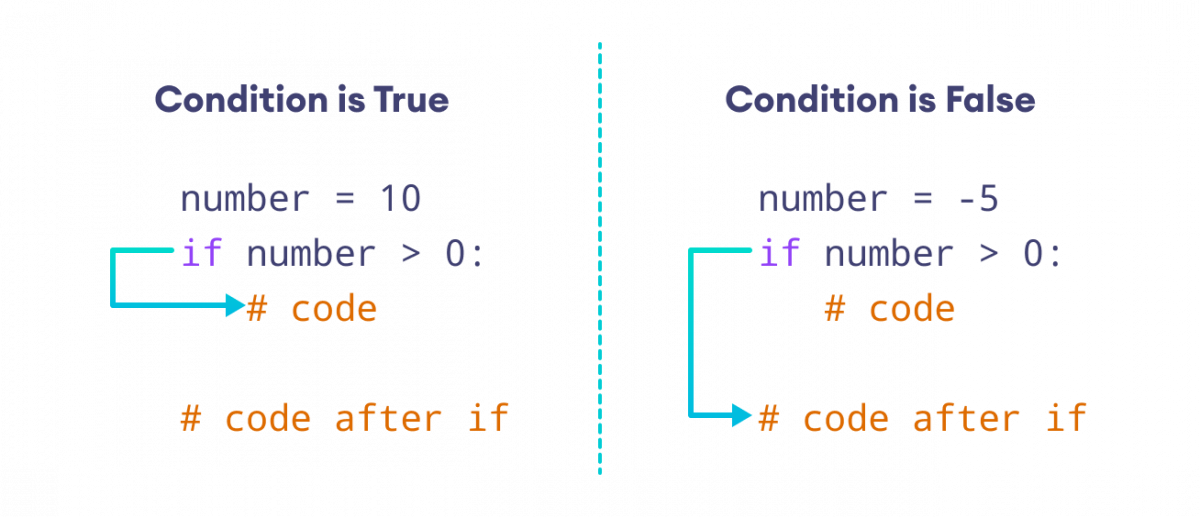
|
| Nested Selection Statements |
Either the true path or the false path includes yet another selection structure

|
| For, While loops |
A for loop is a control flow statement that executes code repeatedly for a particular number of iterations

|
| Procedural Abstraction |
when we write code sections which are generalized by having variable parameters |
| Procedure |
set of instructions that can take parameters (do not have to have parameters and only have ()) and return values or the function |
| Python Def procedures |
 |
| Parameters |
value inputted into a function for the function to produce a result |
| Return Values |
the value that is returned after a function is run |
| Stimulation |
an imitation of a situation or process
Advantages: can be safer, cost-effective, efficient, produce more data
Disadvantages: not as accurate, doesn't include outside factors
|
| Collatz |
The Collatz conjecture is one of the most famous unsolved problems in mathematics. The conjecture asks whether repeating two simple arithmetic operations will eventually transform every positive integer into 1. |
| Hailstone numbers |
The sequence of integers generated by Collatz conjecture are called Hailstone Numbers. Examples: Input : N = 7 Output : Hailstone Numbers: 7, 22, 11, 34, 17, 52, 26, 13, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1 No. |
| Undecidable problems |
An undecidable problem is one that should give a "yes" or "no" answer, but yet no algorithm exists that can answer correctly on all inputs. |
| Unsolvable problems |
An unsolvable problem is one for which no algorithm can ever be written to find the solution. |



