
Q35 Iterative binarySearch of 1D int array
Question 35:
Directions: Select the choice that best fits each statement. The following question(s) refer to the following information Consider the following binarySearch method. The method correctly performs a binary search.
// Precondition: data is sorted in increasing order
public static int binarySearch(int[] data, int target)
{
int start = 0;
int end = data.length - 1;
while (start <= end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (target < data[mid])
{
end = mid - 1;
}
else if (target > data[mid])
{
start = mid + 1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return - 1;
}
int[] values = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 8, 8};
int target = 8;
Purpose
Binary search is an efficient algorithm for finding a specific value in a sorted array or list. We repeatedly divide the search range in half until the target value is found or the range becomes empty. This results in a time complexity of O(log n), making it more efficient than linear search for large datasets.
What is the difference between linear and binary search?
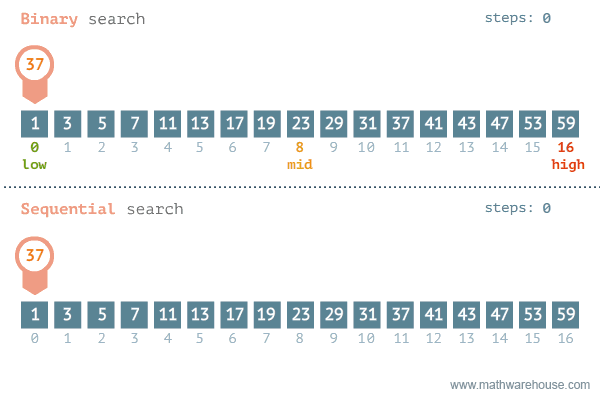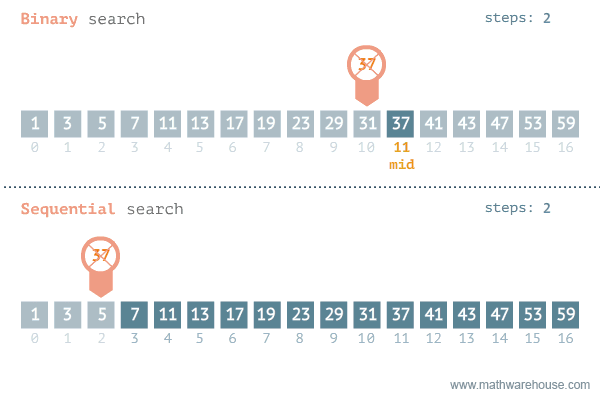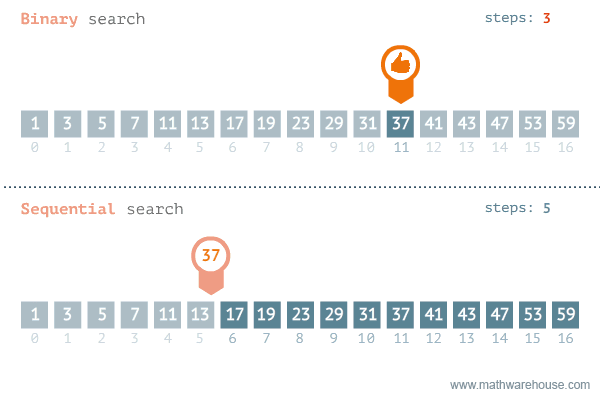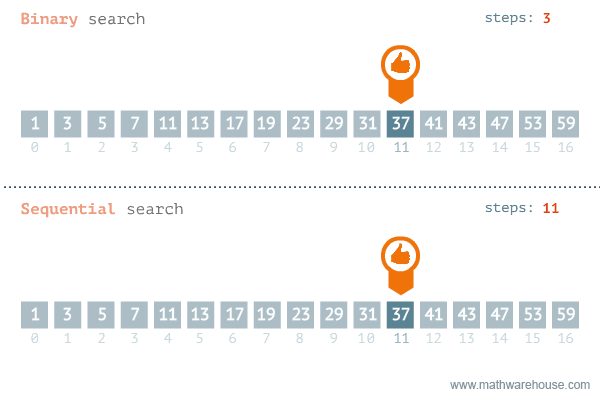
Speed
Binary search is typically much faster than linear sort. We can see that the number of iterations needed to find the target using linear search is 11, while the iterations needed to find the target using binary search is 3.
Java code for iterative binary search is generally the same… Here is an example
public static int binarySearchExample(int[] intArray, int lowPosition, int highPosition, int target){
int midPosition;
// Step 1: Initialize a while loop to continue until the lowPosition is greater than the highPosition
while (lowPosition <= highPosition){
// Step 2: Calculate the middle position of the current range
midPosition = (highPosition + lowPosition) / 2;
// Step 3: Check if the target is greater than the element at midPosition
if (intArray[midPosition] < target) {
// Step 3a: Adjust the lowPosition to search in the right half of the current range
lowPosition = midPosition + 1;
}
// Step 4: Check if the target is less than the element at midPosition
else if (intArray[midPosition] > target) {
// Step 4a: Adjust the highPosition to search in the left half of the current range
highPosition = midPosition - 1;
}
// Step 5: If the target is equal to the element at midPosition, return midPosition
else {
return midPosition;
}
}
// Step 6: If the while loop exits without finding the target, return -1
return -1;
}
Now lets return to the question…
| Iteration | Index | Comparison | New End |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (0 + 7) / 2 = 3 | data[3] < 8 | 4 |
| 2 | (4 + 7) / 2 = 5 | data[5] = 5 | - |
Since data[5] is 8, 5 is returned.
When we run the code in a notebook, we get 5.
binarySearch(values, target)
Question 1: What is the primary advantage of using iterative binary search over linear search?
A. Iterative binary search is easier to implement.
B. Iterative binary search has a faster average time complexity.
C. Iterative binary search is more suitable for unsorted arrays.
D. Iterative binary search guarantees finding the element in the first iteration.
Question 2: In the iterative binary search algorithm, how is the middle position calculated?
A. midPosition = (highPosition + lowPosition) / 2;
B. midPosition = (highPosition - lowPosition) / 2;
C. midPosition = highPosition * lowPosition / 2;
D. midPosition = (highPosition + lowPosition) * 2;
Question 3: What is the time complexity of the iterative binary search algorithm for a sorted array of size ‘n’?
A. O(n)
B. O(log n)
C. O(n^2)
D. O(1)
Question 4: What is the purpose of adjusting the lowPosition and highPosition in the iterative binary search algorithm?
A. To reverse the search direction.
B. To increase the time complexity.
C. To search the entire array in each iteration.
D. To narrow down the search range based on comparisons.
Question 5: If the target element is not present in the array, what value does the iterative binary search function return?
public static int binarySearch(int[] data, int target)
{
int start = 0;
int end = data.length - 1;
while (start <= end)
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if (target < data[mid])
{
end = mid - 1;
}
else if (target > data[mid])
{
start = mid + 1;
}
else{
return mid;
}
}
return - 1;
}
A. -1
B. 0
C. The index of the last element in the array.
D. The target element itself.
Question 6:
public static int iterativeBinarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int low = 0, high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int[] sortedArray = {2, 5, 8, 12, 16, 23, 38, 42};
int target1 = 16;
int result1 = iterativeBinarySearch(sortedArray, target1);
int target2 = 30;
int result2 = iterativeBinarySearch(sortedArray, target2);
What are the values of result1 after executing the code?
A. result1 = 4, result2 = -1
B. result1 = 4, result2 = 5
C. result1 = -1, result2 = 5
D. result1 = 5, result2 = -1
Question 7: What line of code is needed to complete this integrative Binary Search algorithm?
public static int binarySearchExample(int[] intArray, int lowPosition, int highPosition, int target){
int midPosition;
while (lowPosition <= highPosition){
midPosition = (highPosition + lowPosition) / 2;
if (intArray[midPosition] < target) {
<!-- ADD CODE HERE -->
}
else if (intArray[midPosition] > target) {
highPosition = midPosition - 1;
}
else {
return midPosition;
}
}
return -1;
}
A. highPosition = midPosition + 1;
B. highPosition = midPosition - 1;
C. lowPosition = midPosition - 1;
D. lowPosition = midPosition + 1;